
Treatment and functional rehabilitation for physical injuries from sport
Functional rehabilitation aims to return patients to their normal daily, social and sporting life, at an optimal level of performance.
When treating physical sports injuries, it is important to have a multi-disciplinary team, so the patient can progress as swiftly as possible.
Therefore, it is essential that work is coordinated between the various specialists (doctor, physiotherapist, osteopath and trainer), as this enables constant assessment and adaptation of the techniques used and enhances the patient’s progress.
- Details
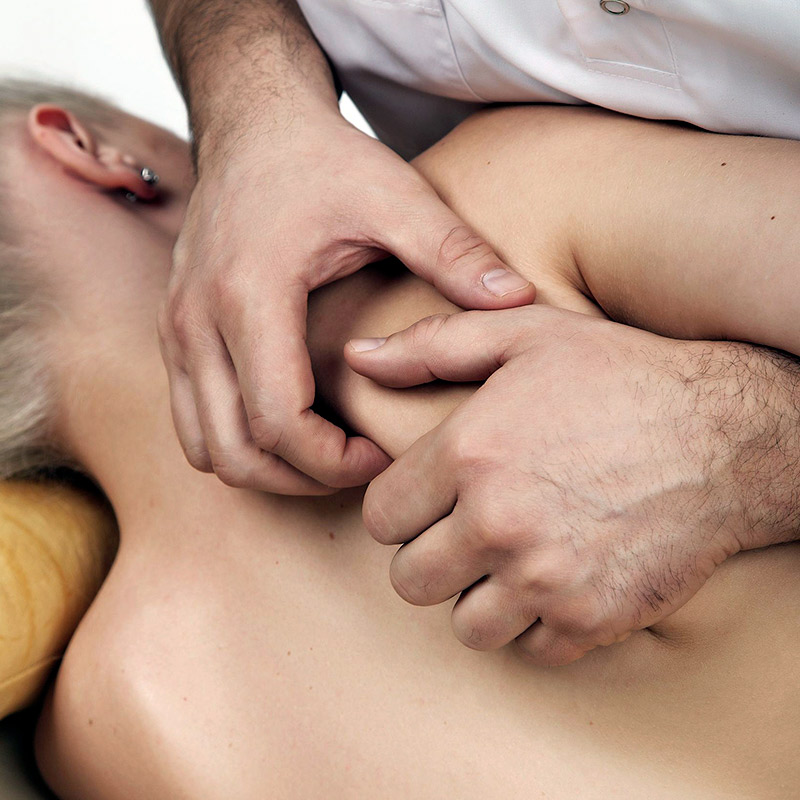
Manual therapies and physiotherapy techniques
Manual therapies improve blood and lymphatic circulation, eliminate toxins, help to repair the different tissues and release adhesions from old injuries, while improving the elasticity of the different tissues. They also accelerate recovery from muscle fatigue after exercise and reduce pain through the release of endorphins.
There are numerous techniques but the common denominator is their action on the locomotor system, increasing the extensibility of the connective structures forming the body’s support framework.
The aim is to help the connective tissue to adapt better to the demands of muscles, tendons and joints. Releasing muscle tension maintains good neuromuscular tone and trains the contraction-relaxation system, which improves immune system function in the long term.
- Details

Pelvic floor physiotherapy
This is a branch of physiotherapy aimed at assessing, treating and preventing potential alterations in the pelvic floor, in men and women. It is of great help in treating various dysfunctions, such as: urinary incontinence, urinary urgency, faecal or flatal incontinence, prolapse, pelvic pain, constipation, sexual disorders, diastasis recti, etc. It is a therapeutic discipline that is useful during pregnancy and postpartum to alleviate aches and pains that occur during and after pregnancy.
On the other hand, for women who practise high impact or hypopressive sports such as running, tennis, athletics or CrossFit, it is used as a complement when there is associated weakness, hypertonia, or stress or mixed incontinence that hampers them from performing the exercise. So, re-educating the perineum, strengthening the muscles and lowering abdominal pressure are the main goals of this therapy.
Medisport physiotherapists who specialise in the pelvic floor use INDIBA Activ, a valuable tool with good results in postpartum issues, pelvic pain and urinary incontinence.
- Details

Lymphatic Drainage
Lymphatic drainage consists of a series of very gentle manual movements to redirect lymph towards the veins and is therefore beneficial for many injuries where there is swelling and/or inflammation.
This massage has a physiological effect on arterial, venous and lymphatic circulation, leading to increased flow and volume, which improves nutrient transport and speeds up the elimination of waste substances and residue from acid catabolism.
Lymphatic drainage is especially indicated for post-traumatic oedema, lymphoedema and post-surgical lymphatic complications, and also accelerates recovery from sports injuries.
We use the INDIBA® therapy together with manual techniques to encourage lymphatic drainage, which relieves pain and improves circulation in the legs, while improving the visual appearance.
- Details

Postural Re-education
This is an active physiotherapeutic treatment, based on performing a series of gentle exercises and general stretches together with breathing and proprioception exercises.
The concept of “chain drives with static function” helps us to understand the method of “Global Postural Re-education”, as we have a series of muscles that are continually working against the force of gravity and therefore influence our posture.
GPR is, above all, a proprioceptive inhibition method, working on the antigravitational muscles, which tend to be shortened and rigid. Attention to breathing is fundamental during this work because the inspiratory muscles also fight against gravity and also have a tendency to become rigid and cause shallow breathing.
- Details

Respiratory physiotherapy
This physiotherapy specialty is dedicated to the prevention, treatment and stabilisation of respiratory dysfunctions or alterations, with the general aim of improving pulmonary ventilation, gas exchange, respiratory muscle function and exercise tolerance. The focusses of this therapy are breathing re-education and reconditioning.
Respiratory physiotherapy effectively treats chronic conditions (COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis and neuromuscular diseases), acute processes (pneumonia, lung abscess) or surgical interventions (transplants and others). The treatment within this specialty is mainly bronchial decongestion, using manual techniques to eliminate excess secretions, and special therapeutic exercise protocols for daily activities.
- Details

